Parallel design in RCT
Parallel study is a type of Randomized Controlled trial (the gold standard of survey in public health and clinical trials) that attempts to compare efficiency of a new treatment/therapy/drug with and existing treatment/therapy/drug. Efficiency is often times measured by observing if there exists a significant improvement of health conditions of patients using the new treatment/therapy/drug over the older one.
The study is then conducted simultaneaously but before each patient is randomly assigned to one treatment group. One of the key advantages of randomization is that It removes selection bias and ensures comparability among groups.
The entire pipeline can be summarized by the following flowcharts:
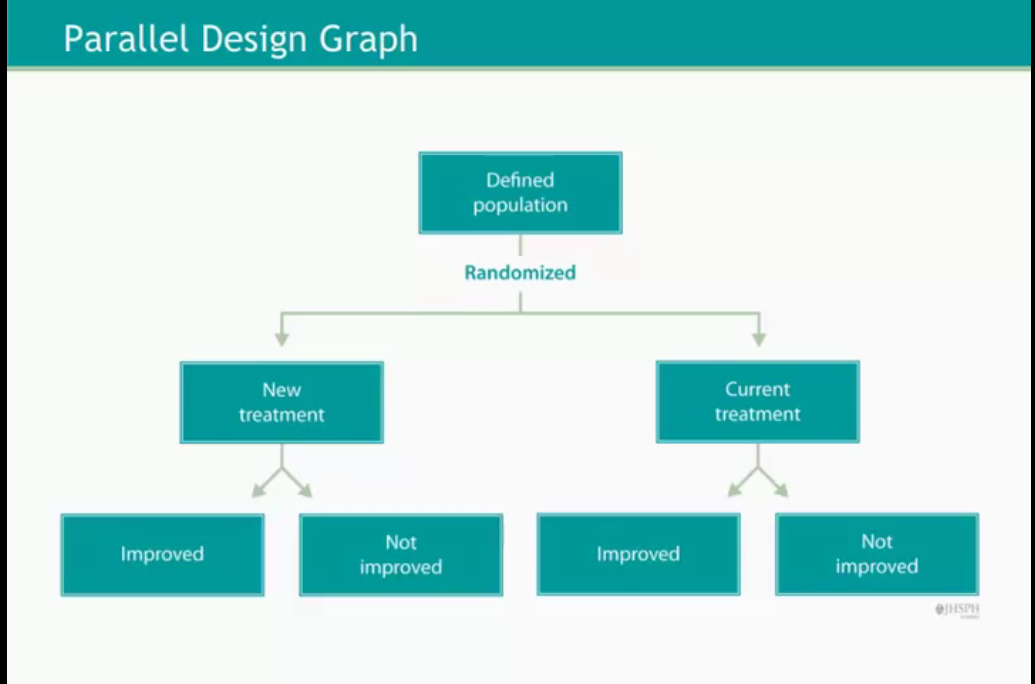
One example of such design is the National Emphysema Treatment Trial (NETT) conducted by the NETT Research group in 1999. A first group of patients is assigned to a treatment that combines lung volume reduction surgery plus a medical therapy while the second group followed a standard therapy control. Duration of follow-up was about 8 years and expectations were to observe mortality reduction and improvement of quality of life for patients in the first group.